Basics of Breastfeeding
What is breastfeeding (Nursing)?
- The feeding of an infant or young child with breast milk
- Directly from female human breasts (i.e. lactation).
- Not from a baby bottle or other containers.
Why breastfeeding?
- Is an unequalled way of providing ideal food for the healthy growth and development of infants,
- Is also an integral part of the reproductive process with important implications for the health of mothers.
When?
- After delivery
- Six months of exclusive breastfeeding.
- Up to two years of age. (Recommended by WHO)
How to start with?
- Understand the physiologic changes of breasts during and after pregnancy.
- Practice certain techniques.
- Perseverance.
Changes in breasts during pregnancy
- First trimester (1-12 weeks)
- Second trimester (13-28 weeks)
- Third trimester (29-40 weeks)
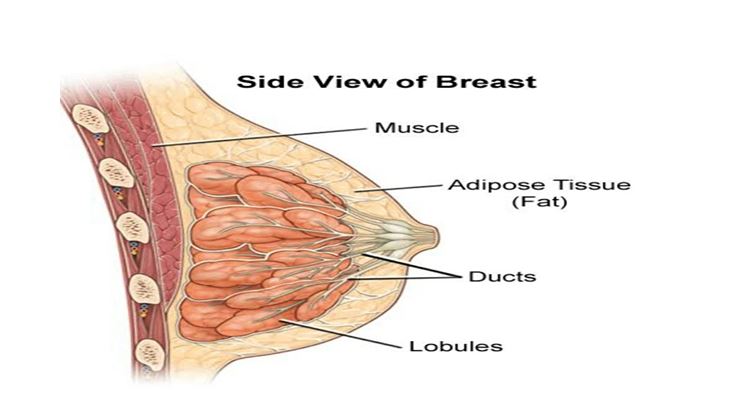
What are breasts?
- A glandular organ located on the chest.
- Made up of connective tissue, fat, and breast tissue (milk glands or mammary glands).
Breast changes: one of the earliest symptoms of pregnancy
- Changes occur due to rising pregnancy hormones and increased blood flow to the breast tissue.
- Changes can be appreciated as early as 1-2 weeks after conception.
What changes occur?
- Enlargement (going up a cup size or two).
- Breasts feel itchy (due to stretching of skin).
- Sometimes mild pain, heaviness or tingling sensation.
- Sensitive nipples.
Blue veins:
- Blood volume typically increases by 50% throughout pregnancy.
- Blue veins typically appear on several areas of skin, including breasts and stomach.
Changes in the breasts in second trimester
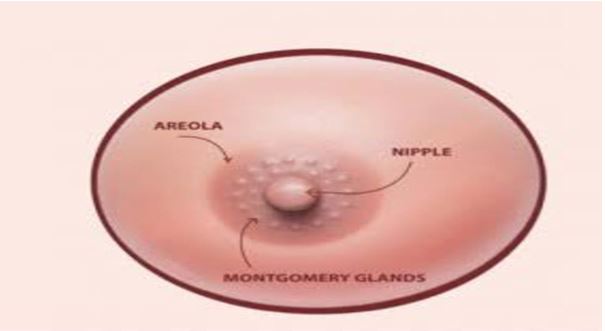
- Darker areolas (colored circles around the nipples) due to hormonal changes.
- Areolar bumps: Painless bumps (Montgomery’s tubercles) lubricate the nipple for easy breastfeeding.
- Nipple discharge: sometimes, not in all.
- Breast lumps: Due to clogged milk ducts.
Changes in third trimester
- Continuing growth – breasts become heavier and larger.
- Colostrum might leak frequently.
- Stretch marks.
- Sometimes may feel tender.
Ways to ease discomfort
- Wearing breast pads for leakage (disposable or reusable).
- Applying lotions and oils (relieves skin tightening and itching).
- Treating blocked milk ducts (mild massage, warm compress to affected area).
- Checking for lumps (self-examination).
- Bra tips:
- Well fitted and good support.
- Wide straps
- Adjustable closure
- No underwire
- Cotton fabric
- Seam free design near nipple
Changes after delivery
- Breasts can become heavier due to milk production.
- Sore and cracked nipples.
- Engorgement.
- Blocked milk ducts.
- Mastitis (painful inflamed breast).
- In case of engorgement or mastitis always consult your doctor and follow further advice regarding continuation of breastfeeding.
- Always have balanced diet and maintain good hydration.